Two View Geometry
August 30, 2022
Planar 2D-2D Geometry (Projective Geometry)
Overview of Perspective Geometry
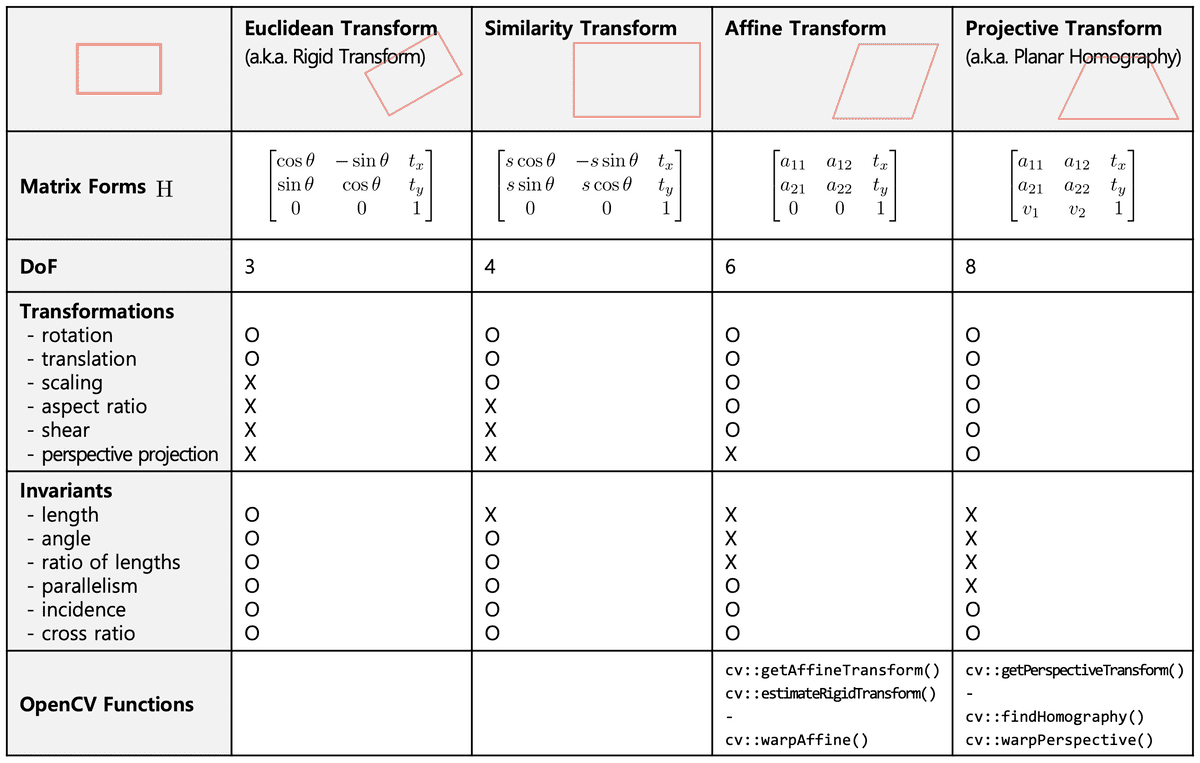
-
Planar Homography Estimation
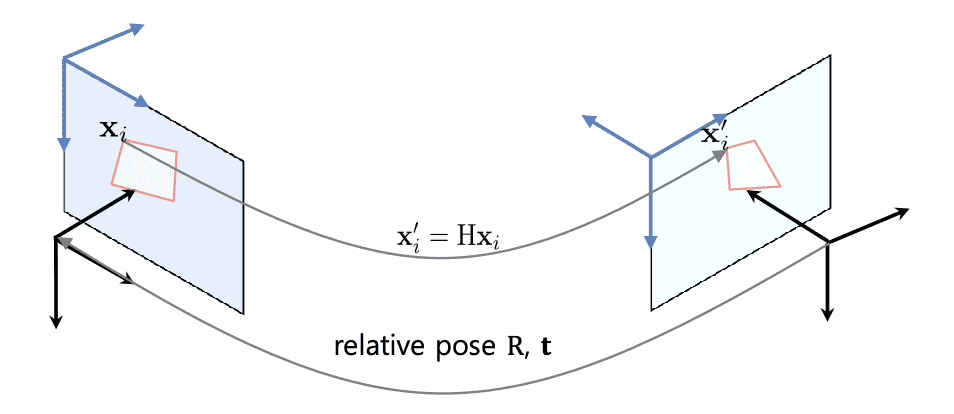
-
Unknown
Planar homography (8 DoF)
-
Given
- Point correspondence
-
Constraints
-
Solutions () ⇒
4-point algorithm- OpenCV cv::getPerspectiveTransform() and cv::findHomography()
-
cf. More simplified transformations need less number of minimal correspondence.
→ Affine (), similarity (), Euclidean ()
-
[Note] Planar homography can be decomposed as relative camera pose.
- OpenCV cv::decomposeHomographyMat()
- cf. However, the decomposition needs to know camera matrices.
-
General 2D-2D Geometry (Epiploar Geometry)
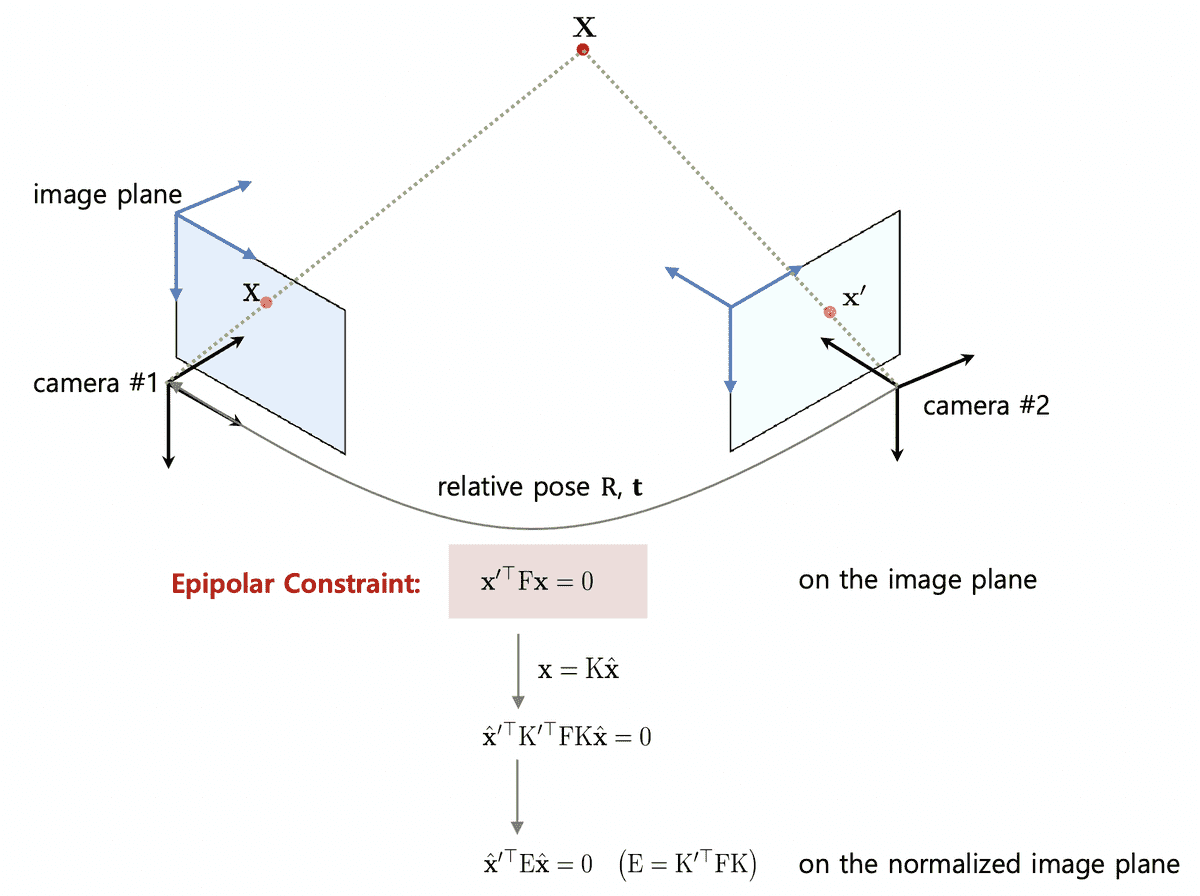
Overview of Epipolar Geometry
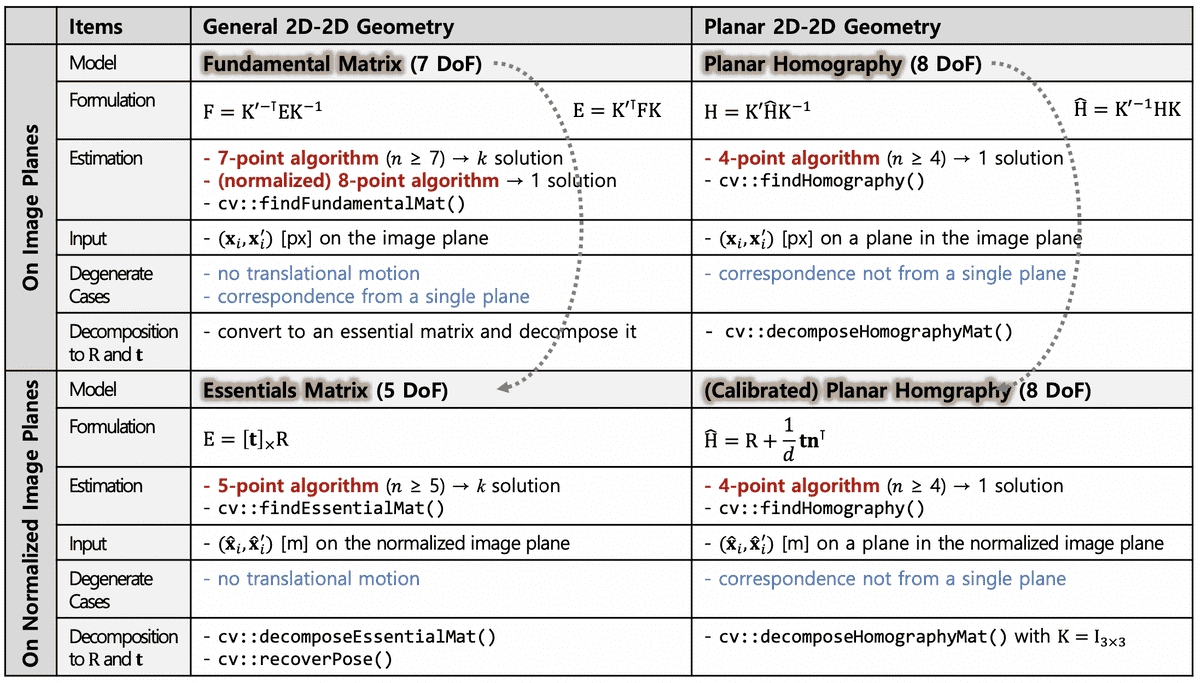
Fundamental Matrix
Essential Matrix
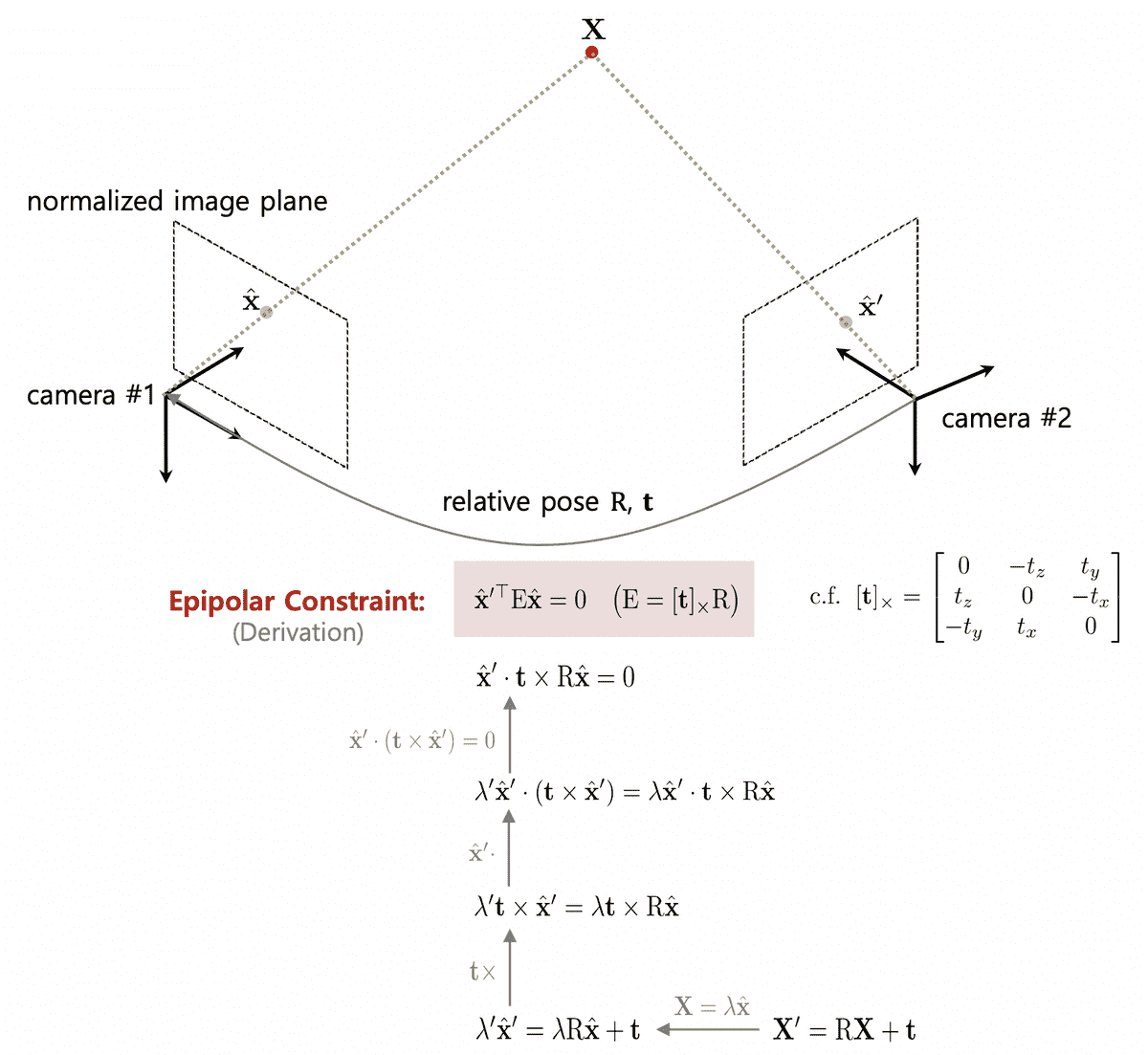
Epiplar Geometry
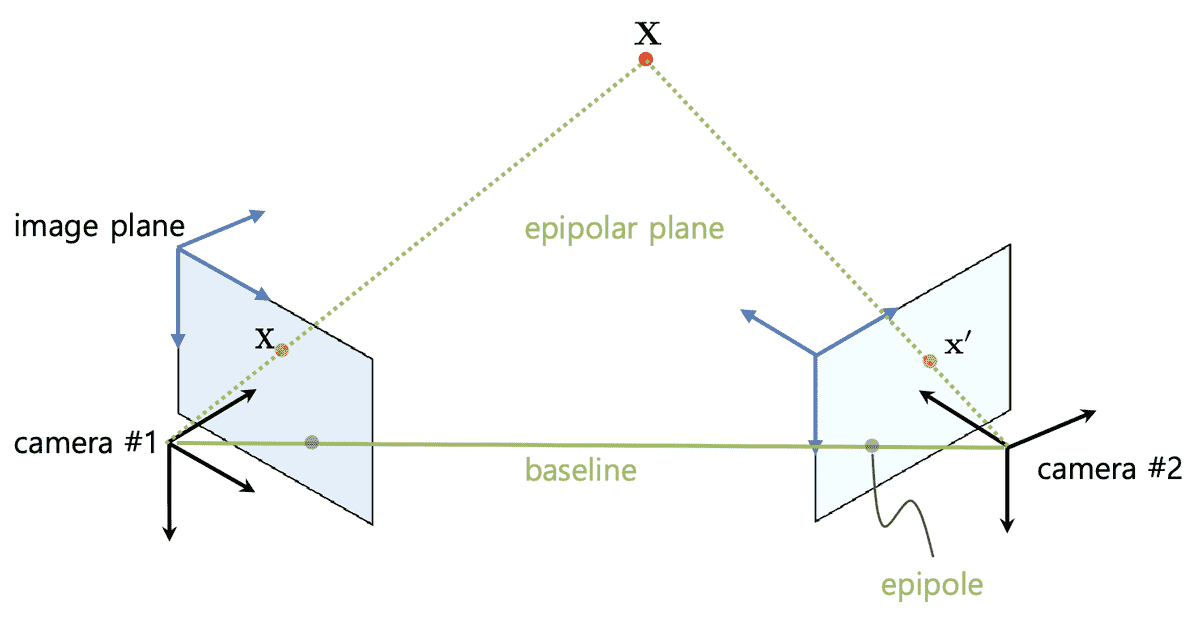
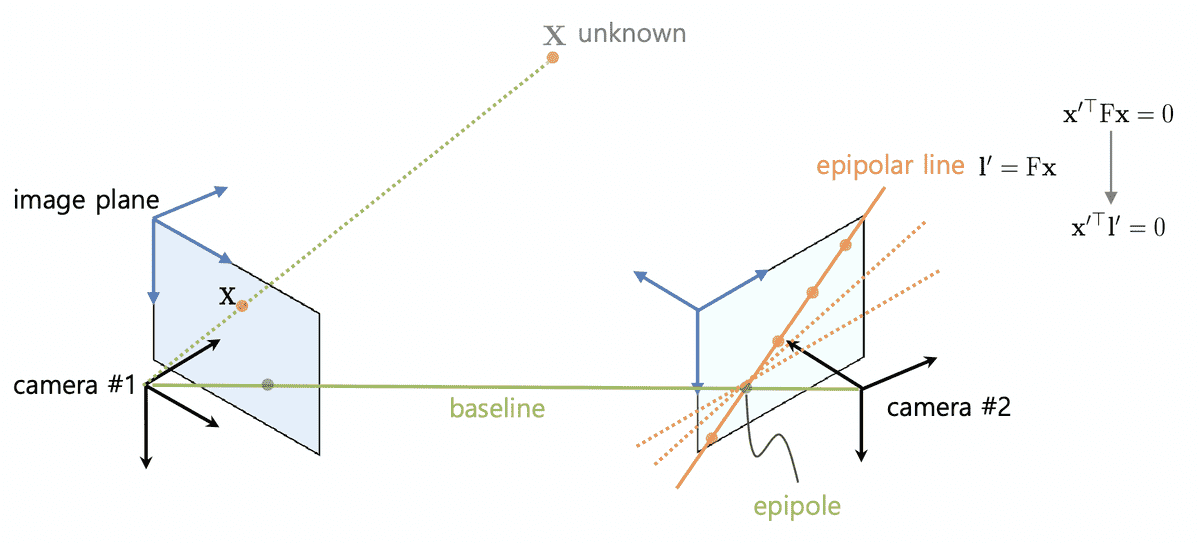
-
Relative Camera Pose Estimation (~ Fundamental/Essential Matrix Estimation)
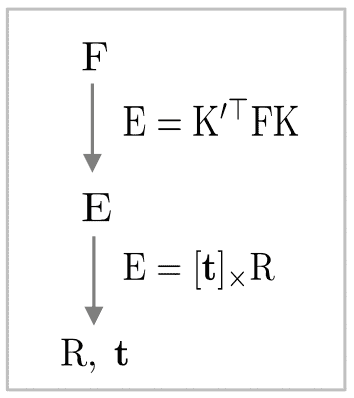
-
Unknown
- Rotation and translation (5 DoF; up-to scale “scale ambiguity”)
-
Given
- Point correspondence
- camera matrices
-
Constraints
-
Solutions (OpenCV)
-
Fundamental matrix: 7/8-point algorithm (7 DoF)
→ Estimation: cv::findFundamentalMat() ⇒ 1 solution
→ Conversion to :
→ Degenerate cases: No translation, correspondence from a single plane
→ intrinsic & extrinsic camera parameters
-
Essential matrix: 5-point algorithm (5 DoF)
→ Estimation: cv::findEssentialMat() ⇒ solutions
→ Decomposition: cv::decomposeEssentialMat() ⇒ 4 solutions “relative pose ambiguity”
→ Decomposition with positive-depth check: cv::recoverPose() ⇒ 1 solution
→ Degenerate case: No translation ()
→ extrinsic camera parameters
-
Planar homography: 4-point algorithm (8 DoF)
→ Estimation: cv::findHomography() ⇒ 1 solution
→ Conversion to calibrated : → Decomposition: cv::decomposeHomographyMat() ⇒ 4 solutions → Degenerate case: Correspondence not from a single plane
→ intrinsic & extrinsic camera parameters + plane normal
-
-
